BREEDING
Sheep and Goat
Reproductive parameters of sheep and goat:
Breeding age | : | 6-8 months |
Comes to heat after lambing | : | after 21 days |
Length of pregnancy | : | 147 days (ranges between 144 and 152 days) |
Male female ratio | : | 1:20 |
Estrous period | : | Every 16-17 days on average in ewes (range 14-19 days). |
Estrous period | : | 19-21 days in does (range 17-24 days) |
Estrous period lasts for | : | About 24-36 hours in ewes and 34-38 hours in does |
USEFUL INFORMATION FOR GOAT BREEDING
1. Use always a pure breed buck on the farm.
2. Buck may be used for mating when attains maturity at about 15 month age.
3. Buck of 18 to 24 months age may be used to serve 25-30 does and when attains full maturity at 2 to 2.5 years of age may be allowed to serve 50-60 does in breeding season.
4. Buck is sexually more active in winter and spring.
5. Buck should not be allowed to serve a doe more than once at a time.
6. Doe attains sexual maturity between 15 to 18 months age, but this period can be reduced by 3 to 5 months by proper feeding and care. Therefore most does will attain sexual maturity at 1 year age.
7. Duration of estrus is 36 hours but in Beetal it is 18 hrs
8. Time of mating or insemination is 0 to 2 hours after onset of heat and a 2nd service again 10 hours if heat continues.
9. Oestrus cycle is of 19 days.
10. The gestation period is of 145-150 days
11. Most does come in heat in September and March.
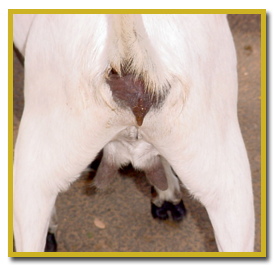
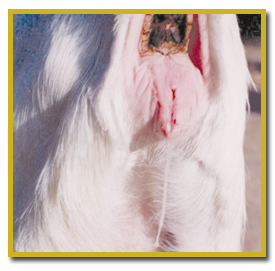
12. Signs of heat
- Redness and swelling of vulva
- Frequent wagging of tail. It may look dirty & wet due to vaginal discharge
- Loss of appetite and reduced feed intake.
- Sudden drop in milk yield.
- Frequent urination
- Excited behaviour of doe
- Mucus thread from vulva
- Frequent bleating
- Mounting by other does in flock.
Two kidding peaks in goats are Jan—April and Sept–Nov.
14. Kids born during January to April grow better than those born during Sept-Nov, suggesting that Aug – Nov matings are better.
15. The male is best for stud purpose at 2 ½ yrs age.
16. Does may be bred at 45 days after normal kidding.
17. The buck when cared well and fed properly keeps fit for breeding purpose till 8-10 years age.
18. The average life span of goat is 12 years.
19. Plan to obtain 3 kidding of does in 2 years for profitable goat farming.
Note:
1. Bucks should not be housed with does.
2. Bringing the teaser buck near the females for a short time every morning generally helpful in picking up those in heat, silent heat/shy breeders.
USEFUL INFORMATON FOR MATING OF SHEEP
1.Detect the oestrus by;
(a) Symptoms: Vulvar swelling, frequent urination, restlessness, reduced appetite.
(b) Teaser: This should be used after applying wet paint on the brisket to teaser ram to spot the ewes in oestrous which carry paint colour mark on the back due to mounting.
2. Follow outbreeding to overcome ill effects of inbreeding.
3. Keep number of ewes per ram of 1 year age 15 to 20.
4. Allow number of ewes for ram of 2 to 2’/2 years age 30 to 40.
Note: In no case for any ram, the number of ewes should not exceed more than 50,
5. Separate ram for about 12 hours in day time and then turn to flock at night for “pen mating”. It is removed during the day and fed separately. “Hand mating” needs more time and labour but ensures covering of each ewe.
6. Usual breeding seasons for sheep
- Summer — March to April
- Autumn — June to July
- Winter — October to November
- Note: Twinning is more when these are bred during spring and autumn of the year
7. The useful breeding period of sheep is up to 5 years, then she is called “broken mouthed”
8. Average oestrus cycle is 17 days (range 14 to 19 days)
9. Average oestrus period, ranges from 30 to 36 hours.
10. Time of ovulation is 12 hours before the end of heat.
11. Gestation period is 147 days (range is 142-152 days).
12. Best time for mating 20 hours after the start of heat preferably in the morning or evening.
13. They breed more with the shortening of day light hours.
14. Maximum useful age of ewe 6 to 7 years.
Note:
1.Lambs born of spring breeding do not have to face extremes of climate and they get more milk from their mothers.
2. Live weight of ewes has direct bearing on lamb production. Heavier ewes at mating give heavier lambs (Mali et. al. 1985); The fertility and litter size are also higher than others (Elcin, 1985)
ESTRUS DETECTION AIDS
DOES:
Signs of estrus:
- Estrus females seek out the mate
- Exhibit constant bleating and restlessness
- Loss of appetite
- Rubbing up against herd mates
- Redness and swelling around the vulva
- Thin mucus discharge from the vulva
Estrus detection aids:
1. Estrus behaviour:
• A rag is rubbed on the bucks scent glands (located caudo medial to horns) and to store this rag in a tightly covered container. When the container is opened and presented to the doe each day; the doe in estrus becomes attracted to it and gets excited by the smell of the rag.
2. Apronised buck:
• Introduction of an apronized buck into a herd of does at the beginning of a breeding season will not only elicit estrus within 5 to 8 days but can also be used to detect does in estrus.
3. Vaginal smears:
• The appearance of more than 50 per cent desquamated, eosinophilic, polyhedral epithelial cells in smear are indicative of estrus.
4. Speculam examination:
• Direct examination of the cervix using a speculum may be more helpful in detecting estrus.
• At the onset of estrus, the vaginal mucosa is reddened and moist, but little mucus is present.
• As heat progresses, a variable amount of transparent mucus is visible in the cervix and on the floor of the vagina which later turns cloudy and finally becomes cheesy white at the end of estrus.
• Conception is best when the doe is bred at the stage when her cervical mucus is cloudy and the cervical os is relaxed.
EWES:
Signs of estrus:
• Ewes will search out the ram and stand to be mounted by him or other ewes but not as often as cattle.
• Rapid tail wagging or raised tail
• Nervousness and increased vocalization
• Decrease in milk production and appetite
• Physical characteristics include, reddened, swollen vulva (not easy to detect because of wool and small size of vulva).
Estrus detection aids:
1. Teaser rams:
• Teaser rams when fitted with a marking harness or brisket paint (paste of paint powder and mineral oil applied to the brisket of the ram) will seek out and breed ewes in heat leaving a mark on the rump of those ewes.
• The ratio of ram to ewe will be 3: 100. In order to avoid breeding vasectomized or apronized rams may be used.
CARE OF REPEAT BREEDERS
1. Change the buck and observe the number of non return.
2. Examine the semen and genital organs and check the quality.
3. Feed properly as follows:
(i) Provide more non legume hay and carrots.
(ii) Supply high phosphate cereals like wheat bran.
(iii) Give iodized salt and phosphorus salt in drinking water.
(iv) Give soft drinking water.
(v) Add vitamin supplement, like Rovi-mix in concentrate mixture rich in protein and energy.
(vi) Give more vitamin— ‘A’.
(vii) Add copper supplement in concentrate mixture.
(viii) Examine blood glucose level of repeat breeders.
(ix) Prevent parasitic infestations.
4. (i) Inject 2 lac pencillin G sodium and 1/2 g streptomycin 12 hours after double insemination.
(ii) Continue the treatment of antibiotics for 3 successive days in severe cases.
5. Allow breeding rest of one heat to pass without mating or insemination
USEFUL INFORMATIONS FOR A.I. IN SHEEP
1. Volume of semen per ejaculate ………..0.8 ml.
2. Total spermatozoa per ejaculate per cu m.m ……. 2 to 3 billion
3. Volume of semen needed for A.I. …………. 0.2 ml.
4. Minimum number of active spermatozoa for fertilization in 0.2 ml semen should be 120 to 150 million.
5. Site for deposition semen-cervix by using specially designed catheter with spirally shaped nozzle.al
The males are attracted by smell, sight and sound and exhibit following behaviour
- Sniff the vulva
- Extending neck with curling of upper lip
- Biting the side of the ewe/doe and wool pulling
- Paw the ewe– raising and lowering of one front leg in a stiff legged striking motion
- Mount and mate