MARKET
Cattle and Buffalo
India is having largest livestock population including Buffaloes, Sheep & Goats, Pigs and Poultry, which are generally used for the production of meat products. India’s meat and meat processing facts particularly registered with APEDA are placed in the below table.
Meat Processing Infrastructure and Related Facts
- APEDA registered Indian Abattoirs cum Meat Processing Plants: 63
- APEDA registered Indian Meat Processing Plants: 63
- APEDA registered Indian Stand-alone Abattoirs: 7
- Number of regular slaughter houses: 1072
- Number of carcass utilization centres: 07
- Small scale meat retail shops: 25,000
- India is the fourth largest buffalo meat exporter of the world with major export destinations (2022-23): Malaysia, Vietnam, Egypt, Indonesia and Iraq.
- India accounts for about 43% of the world buffalo meat production, with Uttar Pradesh producing the most, followed by Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra.
- India is the largest exporter of sheep and goat meat to the world (APEDA, 2021). Major export destinations are United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Kuwait, Maldives and Oman (in descending order).
- Organized poultry sector in India: 80 per cent
- Percent non-vegetarian population in India: 71%
- The current processing levels in poultry are 6%, while for meat it stands at 21%
In the last one-year three new export-oriented units of buffalo, and meat processing have been approved and are reportedly under implementation. In addition, there are few animal casing units engaged in collecting cleaning, grading and exporting sheep and goat and cattle guts.
The individual products under this sub-head are as below:
| Carcasses of Bovine Animals(Fresh) |
| Meat of Bovine Animals With Bone (Fresh) |
| Boneless Meat of Bovine Animals (Fresh) |
| Carcasses of Bovine Animals (Frozen) |
| Meat of Bovine Animals With Bon (Frozen) |
| Boneless Meat of Bovine Animals (Frozen) |
Areas of Production:
The major areas for Buffalo Meat production are Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra and Punjab.
India Facts and Figures :
The country has exported 1,175,869.13 MT of buffalo meat products to the world for the worth of Rs. 25,648.10 Crores/ 3,194.70 USD Millions during the year 2022-23.
Major Export Destinations (2022-23) : Malaysia, Vietnam, Egypt, , Indonesia and Iraq.
DAIRY PRODUCTS
India now has indisputably the world’s biggest dairy industry-in terms of milk production; during 2021-21 India produced close to 221.1 million tonnes of milk, close to 50% than the US and more than three times as much as the much-heralded new growth champ, China. Appropriately, India also produces the biggest directory or encyclopedia of any world dairy industry. The dairy sector in India has shown remarkable development in the past decade and India has now become one of the largest producers of milk and value-added milk products in the world.
The individual products under this sub-head are as below:
| Butter Fresh | Butter MilK |
| Butter Oil | Fresh Cheese |
| Milk & Cream in Powder | Milk for Babies |
| Other Fat | Skimmed milk powder |
| Other milk power | Whole Milk |
| Ghee |
Areas of Production:
Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu are the major production area of Dairy Products in India.
Major Export Destinations (2022-23) :
Bangladesh United Arab Emts, Saudi Arab , USA and Bhutan.
VALUE ADDED MILK PRODUCTS
Value-added Dairy Products
There is a lot of diversity in manufacturing or production of value-added dairy products, out of them some are easy to produce where as other require greater investment in terms of equipment, machinery, training and production time. Some of the common value-added dairy products has been listed below along with short discussion on each of them.
Cheese is quite popular, widely used value-added dairy product. Thousands of cheese varieties are being produced based on flavour, texture and ranging from soft cheeses (mozzarella, ricotta, etc.) to hard cheeses (cheddar, colby, swiss, etc.). Cheese type mainly depends on type of milk used, fat content, fermentation (bacteria or Mold type), processing pattern and ageing.
Yogurt is produced by fermentation of milk, by using bacterial cultures Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. It is becoming more popular because of its health benefits on digestive system. According to European food safety authority (EFSA), yogurt should contain at least 108 CFU live starter microorganisms (Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus) per gram to achieve its health benefits. Flavoured and drinkable yogurts are the widely used yoghurt products.
Butter is water in oil semisolid emulsion made by churning of cream. Organic butter is becoming more popular these days which has been produced from the organic cream, from the cow or buffalo raised on the organic pasture. Salt or food colour may be added to butter. The butter is usually produced from the high percentage fat milk, whereas ghee is a clarified butter, produced by removing water and milk solids.
Ice cream is a very famous “frozen dairy dessert”. It is made with cream, sugar or its alternative, flavour or spice (vanilla or coca), and fruit or nut.
Bottled milk/flavoured milk, bottled raw milk gaining popularity these days among consumers. On farm bottling and sealing prevent chances of adulteration and give more consumer satisfaction. Glass bottles are healthier and eco-friendly option as compared to plastic bottles, as their cleaning and refiling is easy. Whereas flavoured milk is pasteurized or UHT treated milk added with sugar, flavoring and sometimes with food-grade colouring.
Value added functional Dairy products
Functional foods are the foods that provide some additional health benefit because of added functional bioactive compounds to it, beyond providing the basic nutrition. Value-added functional dairy products can be developed as per the requirements of various sections of the population, and there are added benefits. For e.g.
- Functional dairy products which can prevent or slower down muscular atrophy, bone degeneration and indigestion, in geriatric population/elderly people
- Protein-enriched functional dairy foods for growing kids, and children suffering from protein malnourishment.
- Lower lactose or lactose-free formulation/preparation for new-borns and individuals with lactose intolerance
- Whey protein supplements and Sports drinks for athletes and peoples associated with fitness/bodybuilding industry.
- Preparations rich in calories, minerals vitamin, etc. for pregnant/lactating and postmenopausal women’s.
- Low fat functional dairy products containing reduced fat or fat replacers for people suffering from obesity and cardiovascular diseases.
Probiotics
Probiotic are gut friendly microorganism/yeast preparation intended to provide health benefits to the person by improving the indigenous microflora in GI tract. Probiotics mainly contains Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Group bacteria and may contains yeasts such as Saccharomyces boulardii., Predominantally contain lactobacilli group because of their tendency to grow rapidly and tolerate acidic environment. Probiotics have variety of health benefits in the body including, various gastrointestinal conditions like antibiotic assisted diarrhoea, constipation, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel diseases, and diverticular disease. It prevents colic, and necrotizing enterocolitis, and sepsis in infants. Probiotics bacteria by colony formation on the intestinal wall and production of H2O2 and bacteriocins, prevent colonization of pathogenic bacteria, i.e. put ecologic barrier to the pathogenic bacterial proliferation.
Challenges
Value added functional dairy foods can be used as a great tool for providing maximum health benefits from milk and milk products. Value addition to fresh or raw milk can be done at medium or large-scale dairy farm, or at collection centre having continuous supply of raw milk from group of farms, but during these steps various challenges are there:
- Lack of awareness among producers, processors and consumers regarding importance of value addition
- Irregular supply of clean and quality milk for processing
- Insufficient incentives and financial aid to the dairy farmers and entrepreneurs to develop infrastructure for the processing at farm, village and regional levels
- Lack of Training and short courses to the dairy farmers and entrepreneurs at regular interval to develop the processing skills
- Infrastructure for proper marketing of the final product.
CONCLUSION
Milk is a nutrient rich liquid comprises of variety of nutritional components, many of which possess excellent functional and nutritional qualities and can be used to develop value-added functional dairy products. Value addition of milk will provide various health benefit to the society and boost the economy of the farmer and dairy industry simultaneously. Value addition can result in foreign exchange for the country if planned, processed and marketed judiciously following scientific principles. A short course or training may be required for interested candidate before entering into production venture. Trainings are provided by various agricultural institutes of ICAR and the state agricultural universities.
Authors: Dr Dinesh Sharma – Veterinary Surgeon (Government of Haryana), Dr. Rajender Kumar – ICAR-NDRI, Karnal, Haryana
Source: https://krishijagran.com/featured/value-addition-of-milk-and-milk-products/
STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE BUFFALO MEAT INDUSTRY
- Survey projects on production and marketing may be deployed as base material for projection at national and international levels, for the prediction of future trends and for the formulation of meat industry developmental programmes.
- Meat scientists and animal geneticists should collaborate their research aiming at developing a potential cross bred buffalo for meat purpose. Research projects on buffalo meat technology should focus on working slaughter grades of buffaloes as in USDA for beef.
- Buffalo meat affords an easy means of preparing low priced fast meat foods by restricting the cost of raw material. So, the focus area of research should be low cost ready to eat buffalo meat products.
- The other area is to design appropriate technologies to improve the quality of meat from spent animals.
- Research should focus on extension of shelf-life of traditional buffalo meat products available in our country and making necessary efforts for patenting them.
- The Government should encourage and give subsidies/incentives to start meat and by-products processing industries.
- Increasing the production of superior calves through embryo transfer technology, better disease control, adequate nutrition and improved levels of hygiene at meat handling will enable India a quantum jump in meat production by utilizing the surplus male calves.
- Financial institutions should come forward to finance activities related to buffalo meat trade.
- Appropriate consumer education programmes on popularization of quality and health benefits of buffalo meat and products will provide a cheap source of animal protein to the masses.
- The demand for buffalo meat products will serve as a catalyst for all developmental programmes on buffalo meat production.
- A very strong rapport must be built between liaison offices, meat industries, meat corporations, research workers and nodal bodies like APEDA (Agricultural and Processed food products Export Development Authority) and Directorate of Marketing and Inspection (DMI) for exchange of information and overall improvement of meat industry and national economy.
- Government should make efforts to upgrade municipal slaughter houses to semi modern abattoirs with all basic requirements and minimum hygienic standards.
- In the present context of WTO agreement on sanitary and phyto-sanitary (SPS) measures, the hygienic standards of existing meat plants should be improved and made at par with the best in the world.
- The control measures for FMD should be strengthened and adequately controlled areas should be declared as disease free zones to stabilize export market by producing meat for export from such areas.
- The Government should encourage setting up cold storages, supply/value chain and 100% export oriented buffalo slaughter houses in major buffalo belts of the country.
TELANGANA STATE DAIRY DEVELOPMENT COOPERATIVE FEDERATION LIMITED
TSDDCF seeks to usher in an era of rural property in Telangana State through organized commercial dairying based on the principals of cooperatives. To transform itself in to an instrument and vehicle for development of village based dairy sector integrating the milk producers at the village level with the consumer in the urban markets and metropolitan markets.
TSDDCF should facilitate seem less linkage of the milk producer with the milk consumer. The milk producers should own and manage the systems and institutions of procurement, processing and marketing. A dairy farmer owning two or three animals should be in a position to find his livelihood through dairying alone.
Dairy farming should grow into a self-sufficient industry that can support farmers’ livelihoods. TSDDCF will develop into an inbuilt market regulator of milk and milk product prices, giving farmers fair pricing.
Objectives:
- Procuring milk at the Village level and making Payment to the farmer by direct transfer of cash into account as per the FAT & SNF as recorded on the milk analyzers available at every village level collection centers.
- Chilling the milk at clusters village and transporting it to a centralized dairy for pasteurization and further processing.
- Supplying hygienic pasteurized and homogenized pouched milk at the door step of the consumer in Urban, Semi-urban and Rural areas.
- Developing an integrated network of processing facilities in the form of BMCU/MCC and Dairies.
- Developing a strong and extensive marketing network for marketing of milk & milk products.
- Brand positioning and Brand development.
- Supporting the dairy farmer in promoting the milk yield by supplying quality feed, fodder seeds through T.I.P
- Ensuring optimum feed management through Ration Balancing Programme.
Milk Products
- Ghee
- Butter
- Khova
- Doodhpeda
- Sweet Lassi
- Butter Milk
- SFM(Flavored Milk)
- Panner
- Skim Milk Powder
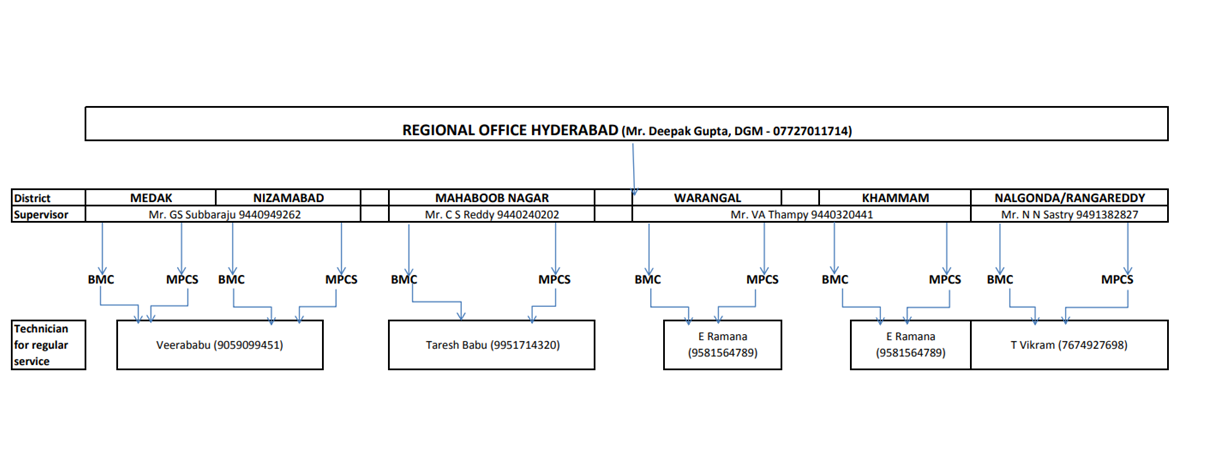
Scheme & Policies
Centrally sponsored Schemes
- National Project for Cattle and Buffalo Breeding
- Livestock Health
- Compendium of Salvaging and rearing of Male buffalo calves scheme
- Livestock Insurance
- Central Herd Registration Scheme
- Directorate of Animal Health (National Programme for Prevention of Animal Diseases)
- Intensive Dairy Development Programme (IDDP)
- Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme (Implemented from 1st September, 2010) (Updated on 09.10.2012)
- Central Sector plan Scheme” Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme”-release of funds to NABARD for its implementation in the country during the year 2012-13 (Updated on 11.06.2012)
- Central Sector plan Scheme” Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme”-release of funds to NABARD under Special Component Plan for Scheduled Caste(SCSC) (Updated on 11.06.2012)
- Central sector plan scheme Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme – the release of funds under North – Eastern Region & Sikkim to NABARD for its implementation in the country (Updated on 11.06.2012)
Livestock and buffalo research stations in India
Central Institute for Research on Cattle | Meerut, Uttar Pradesh |
Livestock Research Station | Mahbubnagar, Telangana |
Livestock Research Station | Lam, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh |
Livestock Research Station | Anand, Gujarat |
Livestock Research Station | Siddarampuram, Andhra Pradesh |
Livestock Research Station | Kattankulathur, Tamilnadu |
Livestock Research Station | Navania, Rajasthan |
Livestock Research Station | Thiruvazhamkunnu, Kerala |
Livestock Research Station | Chittorgarh, Rajasthan |
Central Institute for Research on Buffalo | Hisar, Haryana |
Buffalo Research Station | Venkatramannagudem, West Godavari, Andhra Pradesh |
Buffalo Research Station | Mamnoor, Telangana |
CIRB, sub station | Nabha, Punjab |
KEY FACTS
Communication
- The most important way among buffaloes to communicate is by smell.
- The buffaloes recognize each other by smelling each other.
- Smell is used when marking a territory. Buffaloes will rub themselves against trees to leave scent and they defecate to mark their territory.
- Vocal communication is important especially from calves.
- There are both friendly and hostile vocal communications.
- Posture is important when deciding rank and dominance order.
- A threatening animal will lower and shake its head
